The closing EU CROCODILE video has been released. Featuring Nand Peeters (KU Leuven), Flavia Forte (Eco Recycling) and Zhangqi Wang (Accurec), the video covers the recycling value chain for the recovery and refining of Co from spent Li-ion batteries.
Read More »SOCRATES European Training Network for the sustainable, zero-waste valorisation of critical-metal-containing industrial process residues
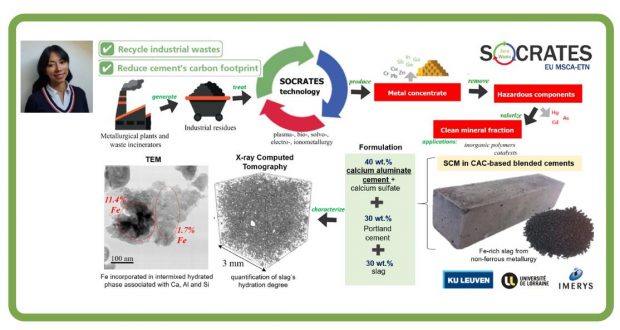
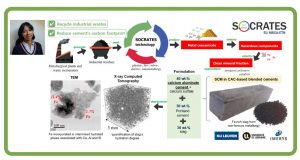
Unlike China, Russia or South Africa, the EU-28 Member States are not in the fortunate position of having vast, easily accessible ore deposits containing valuable metals. However, Europe does have large quantities of secondary industrial residues (tailings, sludges, slags and ashes) that contain significant concentrations of both critical and eco- nomically important metals. The European Training Network for the Sustainable, zero-waste valorisation of critical-metal-containing industrial process residues (SOCRATES) targets ground-breaking metallurgical processes, incl. plasma-, bio-, solvo-, elec- tro- and ionometallurgy, that can be integrated into environmentally friendly, (near-)zero-waste valorisation flow sheets
Read more...
News
Events
-
European Metallurgical Conference EMC 2021
European Metallurgical Conference EMC 2021 - June 27, 2021 - June 30, 2021
Read More »